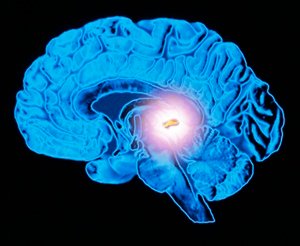
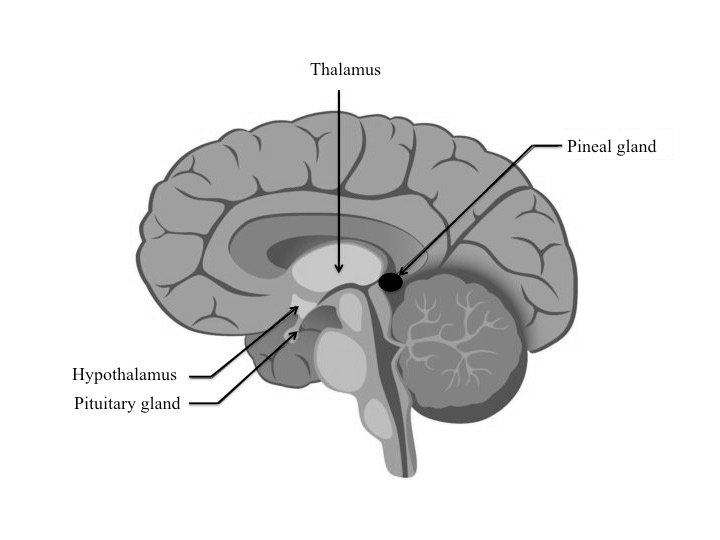
The pineal gland, often referred to as the “third eye,” is a small endocrine gland located near the center of the brain. Despite its diminutive size, this remarkable organ plays a crucial role in regulating our circadian rhythms, sleep-wake cycles, and the production of melatonin, a hormone essential for maintaining a healthy sleep pattern.
In recent years, the pineal gland has garnered significant attention due to its potential impact on our overall well-being. As we delve deeper into the mysteries of this fascinating gland, we uncover its profound influence on various aspects of our lives, from regulating our body’s internal clock to influencing our spiritual and emotional states.
According to research, approximately 70% of adults experience some form of sleep disturbance, which can have detrimental effects on their physical and mental health. By understanding the function and significance of the pineal gland, we can unlock valuable insights into improving our sleep quality, enhancing our overall well-being, and potentially tapping into the deeper realms of consciousness.
Table of Contents
In-depth Exploration of Each Key Point
1. Anatomy and Function of the Pineal Gland
The pineal gland, also known as the “third eye,” is a small, pine cone-shaped endocrine gland located in the brain’s epithalamic region, near the center of the brain. It is primarily composed of pinealocytes, which are specialized cells responsible for producing melatonin, a hormone that plays a crucial role in regulating our circadian rhythms and sleep-wake cycles.
The pineal gland is unique in that it is considered a “neuroendocrine transducer,” meaning it can convert neuronal signals into hormonal signals. This remarkable ability allows the pineal gland to respond to changes in light and dark cycles, which in turn influences the production and release of melatonin.
One of the primary functions of the pineal gland is the synthesis and secretion of melatonin. Melatonin is a powerful antioxidant and plays a crucial role in regulating our sleep-wake cycles, also known as circadian rhythms. When it gets dark, the pineal gland releases melatonin, which induces sleepiness and prepares the body for rest. Conversely, when exposed to light, the pineal gland suppresses melatonin production, promoting wakefulness and alertness.
2. The Pineal Gland’s Role in Sleep and Circadian Rhythms
The pineal gland’s production of melatonin is intricately linked to our sleep-wake cycles, also known as circadian rhythms. These rhythms are governed by an internal biological clock that regulates various physiological processes, including sleep, hormone release, body temperature, and digestion.
When it gets dark, the pineal gland responds by increasing melatonin production. This increased melatonin level signals to the body that it’s time to rest and prepare for sleep. Conversely, when exposed to light, particularly in the morning, the pineal gland reduces melatonin production, promoting wakefulness and alertness.
Disruptions in the pineal gland’s function or melatonin production can lead to sleep disturbances, such as insomnia, difficulty falling asleep, or disrupted sleep patterns. This can have far-reaching consequences on overall health and well-being, as adequate sleep is essential for physical and mental restoration, cognitive function, and immune system regulation.
3. The Spiritual Significance of the Pineal Gland
Throughout history, the pineal gland has been associated with spiritual and mystical significance in various cultures and traditions. Many ancient civilizations, including the Egyptians, Hindus, and Native Americans, revered the pineal gland as a gateway to higher consciousness and spiritual awakening.
In Hinduism, the pineal gland is referred to as the “Ajna Chakra,” or the third eye chakra, and is believed to be the seat of intuition, spiritual vision, and connection to the divine. Similarly, in ancient Egyptian mythology, the pineal gland was considered the “Eye of Horus,” representing the third eye of spiritual vision and enlightenment.
Modern research has shed light on the pineal gland’s role in regulating melatonin production and its potential impact on consciousness and spiritual experiences. Some scientists have theorized that the pineal gland may be involved in the production of endogenous psychedelic compounds, like DMT (Dimethyltryptamine), which could facilitate altered states of consciousness and mystical experiences.
4. Health Implications of a Dysfunctional Pineal Gland
While the pineal gland is small, its proper functioning is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being. A dysfunctional pineal gland can have far-reaching consequences, affecting various aspects of our lives.
One of the primary implications of a dysfunctional pineal gland is the disruption of our sleep-wake cycles and circadian rhythms. Imbalances in melatonin production can lead to insomnia, excessive daytime sleepiness, and other sleep-related disorders, which can have a cascading effect on our physical and mental health.
Impaired pineal gland function has also been linked to various health conditions, including:
| Condition | Description |
|---|---|
| Depression | Melatonin has been found to have mood-regulating properties, and its dysregulation has been associated with an increased risk of depression. |
| Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) | The pineal gland’s response to seasonal changes in light exposure can contribute to the development of SAD, a type of depression that occurs during specific times of the year. |
| Hormonal Imbalances | The pineal gland interacts with other endocrine glands, and its dysfunction can lead to hormonal imbalances, affecting various bodily functions. |
| Neurological Disorders | Some research suggests a potential link between pineal gland dysfunction and neurological conditions like Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis. |
It’s important to note that while the pineal gland plays a crucial role in our overall well-being, its dysfunction is often a symptom of an underlying condition or lifestyle factors. Addressing the root cause and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help support the proper functioning of the pineal gland.
5. Nurturing the Pineal Gland: Lifestyle and Dietary Considerations
To promote the optimal functioning of the pineal gland and support overall well-being, it’s essential to adopt a lifestyle that nurtures this vital organ. Here are some practical tips and strategies:
Lifestyle Considerations:
- Maintain a Regular Sleep-Wake Cycle: Establishing a consistent sleep routine can help regulate the pineal gland’s melatonin production and support healthy circadian rhythms.
- Minimize Light Exposure at Night: Exposure to blue light from electronic devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and computers, can suppress melatonin production. Consider using blue light-blocking glasses or enabling night mode features on your devices.
- Practice Meditation and Mindfulness: Engaging in regular meditation and mindfulness practices can help reduce stress and promote overall well-being, which can positively impact the pineal gland’s function.
- Stay Active and Exercise Regularly: Regular physical activity has been shown to improve sleep quality and support the body’s natural circadian rhythms.
Dietary Considerations:
- Consume Melatonin-Rich Foods: Incorporate foods like tart cherries, goji berries, and seeds (like mustard, flaxseeds, and pumpkin seeds) into your diet, as they are natural sources of melatonin.
- Increase Antioxidant Intake: Antioxidants help protect the pineal gland from oxidative stress and support its proper functioning. Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, and spices like turmeric in your diet.
- Limit Alcohol and Caffeine Consumption: Both alcohol and caffeine can disrupt sleep patterns and interfere with the pineal gland’s melatonin production.
- Stay Hydrated: Adequate hydration is essential for overall health and can support the pineal gland’s function.
By implementing these lifestyle and dietary changes, you can help nurture and support the health of your pineal gland, promoting better sleep, improved circadian rhythms, and overall well-being.
Additional Resources and Further Reading
If you’re interested in exploring the topic of the pineal gland further, here are some recommended resources:
- “The Pineal Gland and Its Hormones” by David S. Goldstein
- “The Third Eye” by Shri Samael Aun Weor
- “Melatonin: Biosynthesis, Physiological Effects, and Clinical Applications” by Dun-Xian Tan
- “The Pineal Gland and Circadian Rhythms” by Josephine Arendt
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
Can the pineal gland become calcified?
Yes, the pineal gland can become calcified, a condition known as “pineal gland calcification” or “brain sand.” This occurs when calcium deposits accumulate in the pineal gland, potentially affecting its function. While the exact causes are not fully understood, factors like aging, environmental toxins, and certain health conditions may contribute to pineal gland calcification.
-
Can the pineal gland be activated or decalcified?
There is ongoing research and debate surrounding the potential activation or decalcification of the pineal gland. Some alternative health practices, such as meditation, yoga, and certain dietary supplements, are believed by some to help activate or decalcify the pineal gland, although scientific evidence is limited. It’s essential to consult with healthcare professionals before attempting any methods that claim to affect the pineal gland directly.
-
Can the pineal gland influence psychic abilities or spiritual experiences?
While the pineal gland has been associated with spiritual and mystical significance in various cultures, there is no scientific evidence to support a direct link between the pineal gland and psychic abilities or spiritual experiences. However, the pineal gland’s role in regulating melatonin and circadian rhythms may indirectly influence our perception and consciousness, which could contribute to altered states of awareness.
Practical Tips and Actionable Advice
To support the health and function of your pineal gland, consider implementing the following practical tips:
-
Establish a Consistent Sleep Routine
Aim to go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends. This helps regulate your body’s internal clock and supports healthy melatonin production.
-
Create a Sleep-Friendly Environment
Ensure your bedroom is cool, dark, and quiet. Consider using blackout curtains or an eye mask to block out light, and invest in a comfortable mattress and pillows.
-
Practice Stress-Reducing Activities
Engage in relaxing activities like meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, or listening to calming music. Reducing stress can positively impact the pineal gland’s function and promote better sleep.
-
Limit Screen Time Before Bed
The blue light emitted by electronic devices can suppress melatonin production. Avoid using smartphones, tablets, or computers at least an hour before bedtime.
-
Incorporate Melatonin-Rich Foods
Include foods like tart cherries, goji berries, and seeds (like mustard, flaxseeds, and pumpkin seeds) in your diet to naturally boost melatonin levels.
By following these practical tips and making lifestyle adjustments, you can help promote the optimal functioning of your pineal gland and potentially improve your overall well-being.
Conclusion
The pineal gland, often referred to as the “third eye,” is a remarkable and enigmatic organ that plays a vital role in regulating our sleep-wake cycles, circadian rhythms, and melatonin production. Its proper functioning is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being, and its dysfunction has been linked to various conditions, including sleep disorders, hormonal imbalances, and neurological issues.
Throughout this article, we have explored the anatomy and function of the pineal gland, its role in sleep and circadian rhythms, its spiritual significance across various cultures, the health implications of a dysfunctional pineal gland, and practical tips for nurturing this vital organ through lifestyle and dietary changes.
As we continue to unravel the mysteries of the pineal gland, it becomes increasingly clear that this small but powerful organ deserves our attention and care. By adopting a holistic approach that prioritizes sleep hygiene, stress management, and a balanced diet rich in antioxidants and melatonin-boosting foods, we can support the optimal functioning of our pineal gland and potentially unlock its full potential.
Remember, the journey towards understanding and nurturing the pineal gland is a continuous process, and each individual’s experience may vary. Embrace the opportunity to explore this fascinating aspect of our existence, and let the mysteries of the “third eye” inspire you to live a more balanced and enlightened life.